Uniting for Peace
➡️ THE UNITING FOR PEACE RESOLUTION - The UN Power to Resolve Stalemates for Global Security
The UN General Assembly's Uniting for Peace resolution was adopted in 1950 as an alternative path when the Security Council is deadlocked due to a lack of unanimity. It allows the General Assembly to act and intervene in the best interests of security and peace, even when it would otherwise be blocked.
The Uniting for Peace resolution has been utilised 13 times between 1951 and 2022. Emergency Special Sessions are then convened to facilitate prompt action, this mechanism can be used by both the General Assembly and the Security Council.
Jump straight to our resources on the ➡️ Uniting for Peace Resolution
Explore our comprehensive guides on -
-
The United Nations & Peacekeeping
-
The 4D Charter
-
The Need for UN Reform
-
Israel's War on Gaza
The idea of a Uniting for Peace resolution was initiated by the U.S. during a time of heightened political tensions when the Security Council was often paralysed by the veto power of its permanent members. Soviet vetoes regarding the Korean War made action by the UN impossible. This new resolution was a way of circumventing the USSR's protest against the UN's recognition of the Republic of China and its pursuit of its own political agenda.
This new resolution shifted dynamics and empowered the General Assembly to recommend actions in times of urgent international crises. The power of the veto was weakened, and the principle of collective security was given priority.
*****

When has the Uniting for Peace Resolution been Invoked?
The resolution has been invoked in several critical situations, the Suez Crisis in 1956 was one of the earliest and most significant examples. The conflict began after the Egyptian President at the time, Gamal Abdel Nasser, nationalised the British and French-owned Suez Canal Company. Joined by Israel, the three countries launched a military invasion of Egypt to regain control.
France and the United Kingdom both vetoed a Security Council resolution calling for a ceasefire. Deadlocked, the General Assembly established the first United Nations Emergency Force. Under the Uniting for Peace resolution, the UN was able to end hostilities and oversee the withdrawal of invading forces.
Other examples:
-
The Soviet invasion of Hungary in 1956.
-
The Lebanon crisis in 1958.
-
During the India–Pakistan dispute over Bangladesh in 1971.
-
South Africa's apartheid policy and the issue of Namibia in 1972.
-
Regarding the crisis in Palestine in 1980.
-
To address the situation in Afghanistan following the Soviet invasion in 1981.
-
Regarding South Africa's occupation of Namibia, also in 1981.
-
Israel's occupation of Palestinian territory, which started in 1997 and has been in continuous session since.
-
The conflict in the Middle East, which again started in 1997, continues to this day.
-
The conflict in Bosnia-Herzegovina, 1993.

The United Nations Charter
The Charter of the United Nations is the founding document of the United Nations. It was signed on 26 June 1945 and mandates the UN and its member states to maintain global peace and security, uphold international law, promote higher standards of living for their citizens, address economic, social, and health concerns, and promote universal respect for human rights and our freedoms.
The UN Charter places the primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security on the Security Council. The Uniting for Peace Resolution helps the council to reinforce the organisation's core mission and also enforces the General Assembly's role in discussing and making recommendations in the event of vetoes. The resolution complements the Charter by removing blockades to multilateral cooperation and collective security.
Limitations of the Uniting for Peace Resolution
One major critique is that the resolution's recommendations, unlike Security Council resolutions, are not legally binding on member states. Without legal authority, effectiveness and compliance can be limited.
The resolution also heavily relies on the will of the General Assembly, which is comprised of the diverse interests of all 193 member states. Critics argue that the resolution may overstep the bounds of the UN Charter and potentially blur the responsibilities of the Security Council and the General Assembly.
The Uniting for Peace resolution was invoked to end the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, however, the non-binding resolutions had more symbolic than substantive value. The UN was effectively ignored by major powers that have the most influence within it (Russia and the U.S.) in the pursuit of their own interests.

The UN's effectiveness relies on the cooperation of its members and their respect for the core values, norms, and international rules set out in the UN Charter. The Secretary General must remain impartial when it comes to the permanent members of the Security Council, as they (Russia) have diplomatic, political, and financial holds over the United Nations.
Regarding Israel's war on Gaza and before the recent Gaza Peace Plan, the Security Council and General Assembly have voted multiple times on resolutions calling for ceasefires in Gaza. The U.S. blocked these resolutions with their veto powers six times, preventing an immediate and permanent ceasefire in Gaza and the release of hostages.
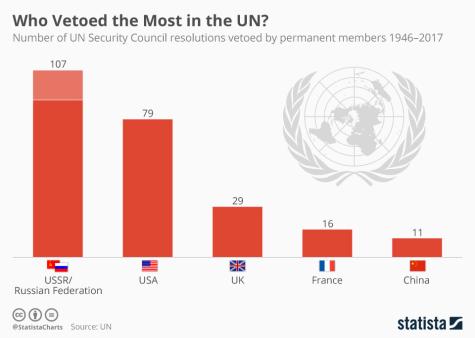
Throughout history, the United States has, in fact, used its veto over 30 times to protect Israel against UN action. The General Assembly's inaction in the situation in Gaza is well noted by human rights and peace experts. Its original mission to maintain global peace and security and uphold international law has been left unmet. Although the Uniting for Peace resolution does not guarantee immediate impact, it at least upholds the UN's legacy and ensures that it remains a respected mechanism for upholding international law.
The Uniting for Peace resolution marks 75 years in 2025, and its contributions to peace and security have been invaluable. In these times of heightened political tensions, polarisation, and militarisation, it's time we start reviewing these mechanisms and putting them to use to counter obstructive power imbalances and nationalist interests that stand in the way of peace.
Author: Rachael Mellor, 22.10.25 licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
For further reading on the Uniting for Peace Resolution see below ⬇️
- Dag Hammarskjöld Library - What is the Uniting for peace resolution?422182
- United Nations General Assembly Resolution 377 (V) in 11/50 - Wikipedia422181
- Audiovisual Library of International Law - Uniting for Peace General Assembly resolution 377 (V) 422183
- Britannica - Peacekeeping, peacemaking, and peace building422185
- #UnitingForPeace422195
- Google News490135
- YouTube Search422196
- Google Scholar490139
- How nonviolent action might save Gaza - IPS 25.09.25490267
- ‘Enough Words’: Colombia’s Petro Urges Armed UN Force to End Gaza Genocide - CD 24.09.25490516
- The UN Turns 80, a Critical Age for People and the UN’s Relevance - CP 19.09.25490268
- Security Council: US votes against resolution on Gaza ceasefire - UN 18.09.25490266
- From Peacekeepers to Naval Convoys: Weighing the Options (and Legal Limits) on More Concerted General Assembly Action on Gaza - Just Security 18.09.25490265
- Uniting for Peace in Gaza: A Test for the General Assembly - OpinionJuris 17.09.25 (must read)490136
- The United Nations Must Act in Gaza Under the Uniting for Peace Resolution - CounterPunch 08.09.25490137
- Uniting for Peace - In a World of Violence, Warmongering on the Rise - How Can We Live Peacefully? - Uniting for Peace 06.09.25491679
- “Uniting for Peace”: How U.N. Could Override U.S. Veto, Send Peacekeepers to Gaza, Block Arms & More - DN 04.09.25490138
- Video: Uniting for Peace Resolution for Gaza - Shagufta Ahmad 28.08.25 (must watch)490140
- How the UN could act today to stop the genocide in Palestine - Mondoweiss 27.08.25 (must read)490328
- Uniting for Peace Resolution for Gaza - Shagufta Ahmad 27.08.25491680
- The United Nations Security Council: Between Powerlessness and Omnipotence - CNRS Éditions 07/25490211
- Multilateralism and the United Nations Security Council: voting, power, and coalition-formation - Palgrave Macmillan 06/25490168
- Questioning the Use of the Veto The Veto Initiative and the General Assembly’s Role as an Accountability Forum for the Security Council - International Community Law Review 0…490186
- The Ukraine War and the Paralysis of the Security Council: Ramifications for Africa’s Common Position on Security Council Reform - Max Planck Yearbook of United Nations Law O…490182
- Empowering the UN Security Council: reforms to address modern threats - Oxford University Press 12/24490212
- Empowering the UN Security Council: reforms to address modern threats - Oxford University Press 09/24490167
- The Security Council Veto in the Context of Atrocity Crimes, Uniting for Peace, and the Responsibility to Protect - Case western reserve journal of international law 06/24490172
- The Reform of the UN Security Council: What Are the Issues? -Brill 05/24490173
- The UN Security Council and the Rejection of Draft Resolutions - Brill 05/24490174
- Judging its Own Case - the Abuse of the Veto Power by Russia - Czech yearbook of public & private international la 12/23490214
- The Conflict in Ukraine and Its Implications for the United Nations System of Collective Security - The Italian Yearbook of International Law Online 11/23490203
- Africa’s Quest for Reform of the United Nations Security Council: A Just Cause Curbed by Unrealistic Proposals - African Journal on Conflict Resolution 08/23490188
- Dangerous Liaisons: The Responsibility to Protect and a Reform of the U.N. Security Council - Columbia journal of transnational law 06/23490198
- The Evolving Role of the General Assembly vis-à-vis the Security Council in the Maintenance of Peace - Journal of International Peacekeeping 05/23490187
- Video: Transatlantic discussion on Uniting for Peace - George Galloway 5/23422201
- The Future We Want? Reflections on the Exercise of the United Nations Security Council Members’ Veto Powers towards the International Criminal Court - Max Planck Yearbook of …490213
- Journal: Power Shift: The Return of the Uniting for Peace Resolution - Michael P. Scharf (2023)422186
- Video: Douglas Roche: ‘Uniting for Peace’ at the United Nations 6/22422198
- Video: What is Uniting for Peace? Can it Stop the War in Ukraine? - Noah Zerbe 3/22422197
- Bargaining in the UN Security Council : setting the global agenda - Oxford University Press 02/22490164
- Existing Legal Limits to Security Council Veto Power in the Face of Atrocity Crimes - The Journal of international law and diplomacy 01/22490184
- Beyond the Veto Roles in UN Security Council Decision-Making - Global Governance: A Review of Multilateralism and International Organizations - Brill 02/21490199
- Looking beyond R2P for an Answer to Inaction in the Security Council - Florida journal of international law 11/21490197
- Saving succeeding generations from the scourge of war: the United Nations Security Council at 75 - Brill Nijhoff 10/20490166
- Existing legal limits to Security Council veto power in the face of atrocity crimes - Cambridge University Press 08/20490162
- The Security Council Veto in the Context of Atrocity Crimes, Uniting for Peace and the Responsbility to Protect - Case Western Reserve Journal of International Law 06/20490163
- Innovating to Restrain the Use of the Veto in the United Nations Security Council - Case Western Reserve Journal of International Law 06/20490176
- United Nations Security Council Permanent Membership and the Veto Problem - Case Western Reserve Journal of International Law 06/20490175
- Responding to Atrocity Crimes and the Security Council’s Veto Power: Implications, Realities, and the Future - American Society of International Law 06/20490195
- Questioning Unlimited Veto Use in Face of Atrocity Crimes - Case Western Reserve Journal of International Law 06/20490191
- Elected members of the security council: lame ducks or key players? - Brill 01/20490208
- Elected members of the security council: lame ducks or key players? - Brill Nijhoff 01/20490165
- The penholder system and the rule of law in the Security Council decision-making: Setback or improvement? - Leiden Journal of International Law 11/19490177
- Negative surprise in UN Security Council authorization: Do the UK and French vetoes influence the general public’s support of US military action? - Journal of Peace Research …490181
- The rule of law in the United Nations Security Council decision-making process: turning the focus inwards - Routledge 01/19490180
- Overcoming Russian and Chinese Vetoes on Syria through Uniting for Peace - Journal of Conflict and Security Law 01/19490206
- The Responsibility Not to Veto Revisited: How the Duty to Prevent Genocide as a Jus Cogens Norm Imposes a Legal Duty Not to Veto on the Five Permanent Members of the Security…490196
- Would a Code of Conduct for the UN Security Council Make Its Response to Mass Atrocities More Consistent and Accountable? - Humanitäres Völkerrecht : Informationsschriften …490200
- Separating Intervention from Regime Change: China's Diplomatic Innovations at the UN Security Council Regarding the Syria Crisis - The China Quarterly 06/18490185
- The Security Council veto and Syria: responding to mass atrocities through the “Uniting for Peace” resolution - Indian Journal of International Law 05/18490170
- United States Vetoes Security Council Resolution Declaring Israeli Settlements Illegal - American Journal of International Law 09/17490189
- The establishment of the Peacebuilding Commission: reflecting power shifts in the United Nations - International Peacekeeping 11/16490219
- The Responsibility not to Veto: a Responsibility too far? - Oxford University Press 08/16490204
- When the Security Council is divided: Imprecise Authorizations, Implied Mandates, and the "Unreasonable Veto" - Oxford University Press 06/16490193
- Responsibility to recommend: the role of the UN General Assembly in the maintenance of international peace and security - Journal on the Use of Force and International Law 06…490209
- The Responsibility Not to Veto Revisited : How the Duty to Prevent Genocide as a Jus Cogens Norm Imposes a Legal Duty Not to Veto on the Five Permanent Members of the Securit…490215
- A Vetoed International Criminal Justice? : Cursory Remarks on the Current Relationship Between the UN Security Council and International Criminal Courts and Tribunals - Dirit…490220
- Assessing the influence of the Responsibility to Protect on the UN Security Council during the Arab Spring - Cooperation and Conflict 11/15490190
- The UN Security Council in the twenty-first century - Lynne Rienner Publishers 10/15490207
- Chinese diplomacy and the UN Security Council : beyond the veto - Routledge 08/15490169
- Russia's Veto in the Security Council: Whither the Duty to Abstain under Art. 27(3) of the UN Charter? - Zeitschrift für ausländisches öffentliches Recht und Völkerrecht …490194
- R2P and the "Abusive" Veto : the Legal Nature of R2P and its Consequences for the Security Council and its Members - Austrian review of international and European law 10/14490201
- Deadlock or Restraint? The Security Council Veto and the Use of Force in Syria - Journal of Conflict and Security Law 09/14490171
- “Uniting for Peace”: Does it Still Serve Any Useful Purpose? - AJIL, Cambridge Press 2014422184
- How Many is Greater than Five: A Comprehensive Model Proposal for the United Nations Security Council - Turkish Journal of International Relations 08/14490183
- The ‘Responsibility Not to Veto’, Secondary Rules, and the Rule of Law - Global Responsibility to Protect 07/14490205
- A Keen Observer of the International Rule of Law? International Law in China's Voting Behaviour and Argumentation in the United Nations Security Council - Leiden Journal of I…490210
- Unblocking the UN Security Council The Uniting for Peace Resolution - Journal of Conflict and Security Law 08/13490179
- The Responsibility to Protect and the Permanent Five: the Obligation to give Reasons for a Veto - Pallas Publications 12/11490216
- Unreasonable Veto as a Challenge to the Global Order - Journal of international law 2/07490217
- The Security Council: Paralysis, Reform, and the Future - Pouvoirs 1/04490202