Autocracy

The Rise of ➡️ AUTOCRACY
Autocracy is a form of governance in which absolute power resides in the hands of a single individual. Democratic backsliding has accelerated since 2016 and has infiltrated all corners of the world.
Jump straight to our resources on ➡️ Autocracy
Explore our comprehensive guides on -
Examples of modern autocrats include Viktor Orbán, Vladimir Putin, Nayib Bukele, Narendra Modi, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, Xi Jinping and Nicolás Maduro.
They do not take power through military coups but by quietly undoing core democratic principles, weakening the rule of law, spreading disinformation campaigns, creating confusion, and dismantling democracy from within.
Autocratic leaders prioritise control over individual freedoms and public participation. They open the doors for abuse of power, impunity, and the suppression of dissent.
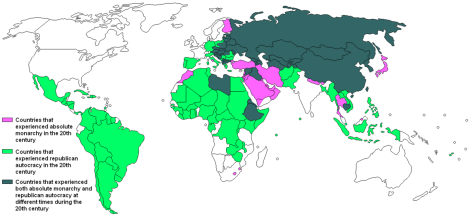
Autocracy Throughout History
Autocracy was one of the first forms of governance. The Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs exemplified early autocratic rule, where a single individual was not only the political leader but also revered as a divine entity.
Similarly, at its peak, the Roman Empire saw emperors wielding vast powers, often unchecked by senatorial constraints. In medieval times, monarchies across Europe were ruled by kings and queens who ruled unquestioned over their realms.
Autocracy provided stability and order in chaotic times when civilisations had never known democratic rule. Autocrats were able to maintain power and control citizens through propaganda and indoctrination. They legitimised their rule using religion, birthright and the threat of foreign hostility.
In the 19th century, dictatorships became more common, beginning with the caudillos in Latin America and the empires of Napoleon and Napoleon III in Europe. Fascist and communist states developed in the 20th century, characterised by authoritarian leaders such as Stalin, Hitler, Mussolini, and Kim Il Sung.

Autocracy vs. Oligarchy
An oligarchy is a form of government controlled by a small group of elites. They hold power and influence because of their financial, social, or political status. Autocrats and oligarchs are similar in that they both deny the general population access to power, authority, and independence. Elite individuals or families wield control for the benefit of their own class, ignoring the needs of the greater good.
Modern oligarchies are typically heavily influenced by the owners of large corporations whose considerable financial contributions give them huge weight in policymaking. Examples today include Russia, China, Iran and increasingly so, the U.S. under the presidency of Donald Trump and tech billionaire Elon Musk. The involvement of Musk in Trump's presidential campaign and influence after his inauguration is a prime example of the rich and powerful being granted unfettered access to elected officials.
Autocracy – The Good and Bad
One potential advantage of autocracy is the ability it grants those in power to make quick decisions, avoiding lengthy debates and bureaucratic red tape. Rapid implementation of new policies can be crucial in times of crisis or for implementing large-scale projects efficiently, as demonstrated by China. Centralised authority also ensures stability in governance.
These advantages are often overshadowed by significant drawbacks for civilians living in autocratic societies. The lack of checks, accountability, varied input, and regulations can easily lead to the abuse of power, corruption, and massive suppression of dissent. With no responsibility to the people, policies often fail to reflect the will or needs of citizens. Autocratic societies struggle with societal discontent, unrest, conflict, and human rights violations.

Modern Autocracies
In today's digital age, modern autocracies have leveraged technology to maintain control and legitimacy. Autocratic regimes will manipulate surveillance technologies to monitor and suppress dissent. They are also able to use censorship, algorithms, and artificial intelligence to easily control the media and communications, denying a population transparent and objective information.
The internet can be used to push state narratives and obstruct opposing viewpoints. Soft autocracy is a strategy where governments maintain the façade of democratic processes, such as elections, while manipulating outcomes to ensure their own agendas and retention of power.
Russian President Vladimir Putin exemplifies modern autocracy, having maintained power since 2012. Through various constitutional amendments, media control, domestic repression, and a strong security presence, his leadership has stripped Russia of democratic freedoms and dragged the country into a full-scale war with Ukraine.
In North Korea, Kim Jong-un continues the legacy of one of the world's longest-running dynastic dictatorships. The Kim family has ruled North Korea since 1948, and under the current leader, Kim Jong-un, the country remains one of the world's poorest nations. Elite families hold the vast majority of wealth and exert heavy influence over the economy.
Kim Jong-un has served as supreme leader since 2011 and since then has consolidated his power by systematically purging numerous top officials. Eliminating potential threats and appointing party and military elites to key posts has been a key strategy to ensure the survival of his repressive regime.
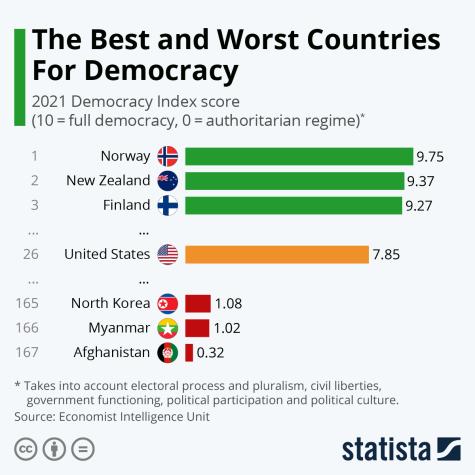
Democracy is currently under threat all around the world. In 2023, global freedom declined for the 18th consecutive year across all regions. Growing political polarisation and the rise of populist authoritarian leaders pose major challenges to fair elections, freedom of expression and assembly, press freedom, and the rule of law.
Democracy paves the way for security, stability, and prosperity. We must not allow democratic institutions to be weakened. We must fight for free and fair elections and peaceful transitions of power and ensure that journalists and whistle-blowers are protected and their stories heard.
Author: Rachael Mellor, 10.06.25 licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
For further reading on Autocracy see below ⬇️